Global consumption of resources is increasing at an alarming pace, this rate of consumption is not sustainable as the earth cannot regenerate the materials and natural resources at that rate. Between 1950 and 2005, worldwide metals production grew six fold, oil consumption eight fold, and natural gas consumption 14-fold. If global consumption continues at the same rate, the future generations will not have the same resources available to them that we have now.
It is imperative that manufacturing industries strive for ‘Sustainable Manufacturing’.
Sustainable manufacturing Defined
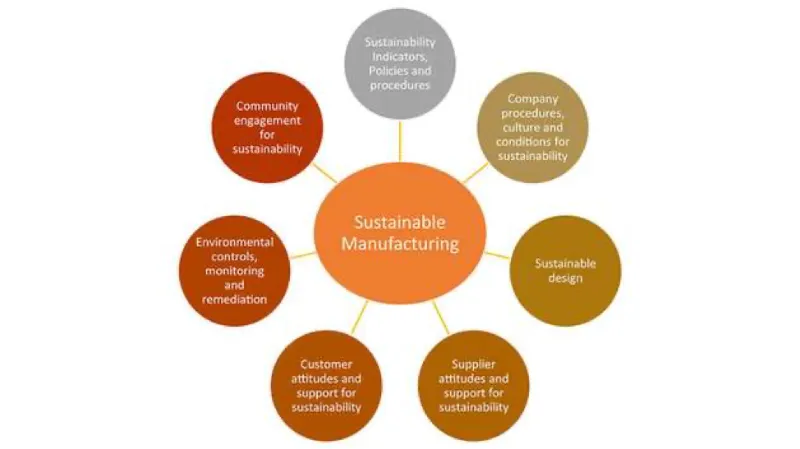
Sustainable manufacturing (SM) or green manufacturing can be defined as a method for manufacturing that minimizes waste and reduces the environmental impact. These goals are to be obtained mainly by adopting practices that will influence the product design, process design and operational principles. Therefore, sustainable manufacturing may be defined as a system that integrates product and process design issues with issues of manufacturing, planning and control in such a manner as to identify, quantify, assess, and manage the flow of environmental waste with the goal of ultimately reducing the environmental impact to that of the self-recovery capability of the Earth could deal with while also trying to maximize resource efficiency.
Sustainable Manufacturing (SM) Processes
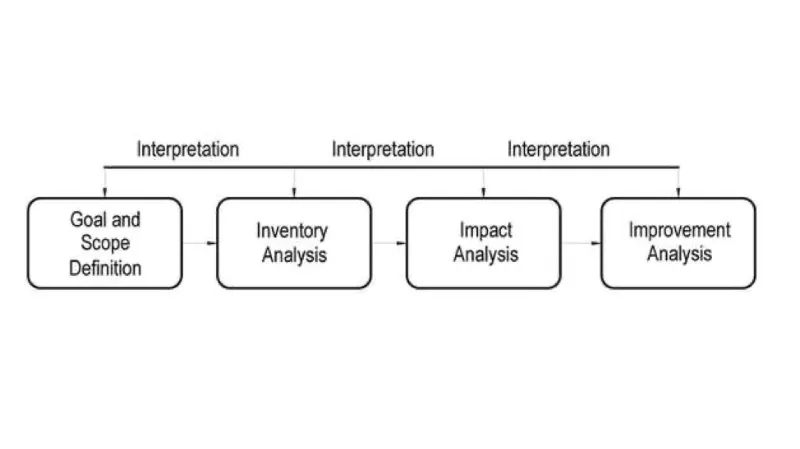
Processes generally used to implement SM is the Life Cycle Assessment (LCA). It is a process to fully examine the environmental impact of different activities performed by industry including the production of goods and services. LCA can be applied for any activity that is either at national level or global level in order to identify environmental burdens resulting from the activities of a society, region or industrial sector. LCA can provide insight for the engineer to study any given product and can identify the methods to reduce the environmental impact of a specific product or process.
Sustainable Manufacturing In Practice
GFES requires that all its manufacturing include the following four activities:
- Energy use reduction
- Responsible water use
- Emissions reduction
- Responsible carbon foot print reduction
- Waste generation reduction
Sustainable manufacturing integrates sustainable activities at all levels of manufacturing – product, process and system. GFES not only considers the 3R’s: to reduce, reuse and recycle, but considers the expanded 9R form as well: reduce, reuse, recycle, recover, redesign, remanufacturing, repurpose, refurbish, and refuse.
GFES’s Manufacturing processes and systems consider sustainability at every level, so that there will be comprehensive adherence to sustainability principles. All the processes used are energy efficient while maintaining requisite quality. All the interconnected systems also share the same philosophy. Reduce energy intensity and emissions in all operations and the supply chain. Zero-emission (i.e. closed-loop) manufacturing views the manufacturing system as an industrial ecosystem, and requires the reuse of wastes or by-products within the manufacturing system. Manufacturing systems employed have the flexibility for material substitution, and accommodate variations in material flows to assist in enhancing sustainability while maintaining competitiveness. To reduce the environmental impacts of manufacturing processes, it is often necessary to optimize the environmental performance of the existing processes as well as develop new green processes.
In industry, manufacturing processes are generally designed for high performance and low cost with little or no attention paid to environmental or sustainability issues. Optimization of manufacturing processes are done only in reference to minimizing the machining time or cost with no environmental consideration.
Development of New Sustainable Processes
GFES focuses on improving and optimizing the existing industry processes, we believe it is important to develop new processes that use less harmful materials and generate fewer emissions.
GFES
- GFES has made long-term commitment into sustainable Qualified Opportunity Zone (QOZ) Manufacturing.
- GFES believes in working within the Environmental, Social, & Governance (ESG) model for manufacturing and development.
- GFES has committed substantial resources to create jobs in sustainable manufacturing
- GFES has worked with Federal, State and Local governing bodies to maximize jobs creation.
- GFES has made long-term commitments in jobs creation in sustainable manufacturing
https://www.industr.com/en/sustainable-manufacturing-principles-applications-and-directions-2333598